



 For further study (only because several people asked for more info on social media - I won't personally be discussing this topic on this platform):
For further study (only because several people asked for more info on social media - I won't personally be discussing this topic on this platform):

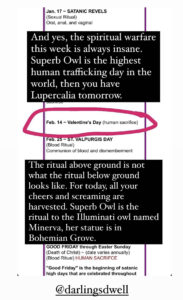


…let he who has ears…




 For further study (only because several people asked for more info on social media - I won't personally be discussing this topic on this platform):
For further study (only because several people asked for more info on social media - I won't personally be discussing this topic on this platform):





 Truths about Masks that Politicians and the BBC Probably Forgot to Mention
1) Face masks have been proven to do harm but not proven to do good. Forcing citizens to wear them is a form of oppression. Support for mask wearing comes from individuals promoting face masks for political rather than health reasons. There is now considerable support for masks to be worn out of doors and even in the home. There is absolutely no scientific reason for this.
2) Over a dozen scientific papers show clearly that masks are ineffective in preventing the movement of infective organisms. They also reduce oxygen levels and expose wearers to increased levels of carbon dioxide.
3) Nine medical authors from Australia and Vietnam studied cloth face masks and concluded that cloth masks should not be recommended for health care workers.
4) Wearing a mask for long periods could cause pulmonary fibrosis. Loose fibres are seen on all types of masks and may be inhaled causing serious lung damage.
5) Researchers in France proved that wearing a surgical mask causes breathlessness.
6) Masks should be changed every couple of hours and old masks should be disposed of safely. If cloth masks are worn, they should be washed at high temperatures twice a day. Disposable masks should be discarded after one use. (Masks thrown down in the street are a serious health hazard.)
7) Evidence proving the danger and ineffectiveness of masks has been banned, blocked or deleted. Discussion and debate about the value of face masks is suppressed.
8) In September 2020, 70 Belgian doctors claimed that mandatory face masks in schools are a major threat to child development.
9) A leading German virologist claims that face masks are a wonderful breeding ground for bacteria and fungi.
10) Dentists in New York have reported that mask wearing causes gum disease and dental cavities. The dentists say that face coverings lead to mouth dryness and an increase in the build-up of bacteria.
11) Exemption certificates/cards can be obtained online for those who are unable to wear a mask.
12) Some face masks may have pores five thousand times larger than virus particles.
13) Masks should never be touched once in place. If a mask is touched it must be replaced immediately.
14) No one should wear a mask while exercising. There have been several reports of masked children dying while exercising. There is evidence showing that mask wearing reduces blood oxygen levels even when the wearer is standing still. Individuals who exercise are likely to sweat. Masks then become damp more quickly and the damp promotes the growth of microorganisms.
15) There is a risk that viruses may accumulate in the fabric of a mask – thereby increasing the amount of the virus being inhaled.
16) Putting a mask on a baby or unconscious patient is dangerous. The mask may result in the wearer choking on vomit.
17) Some of the carbon dioxide exhaled with each breath is trapped behind the mask.
18) One study of health workers wearing masks showed that a third developed headaches requiring painkillers. Another study showed that 81% developed headaches – and their work was affected.
19) A mask can reduce blood oxygenation by up to 20% – leading to a possible loss of consciousness. At least one road crash has been blamed on a driver wearing a mask. Police reported that the driver of a single car crash in New Jersey is believed to have passed out behind the wheel after wearing a mask for too long.
20) Over a dozen studies failed to show that wearing a mask provides protection against infection.
21) Masks are being used as a conditioning tool to make us more compliant.
22) A study of 53 surgeons showed that there were statistically significant falls in blood oxygen levels after masks had been worn for a few hours. It is important to remember that surgeons who wear masks (and not all do) work while standing, rather than walking, and they work in a controlled, air conditioned environment. They do not touch their masks and they change them regularly.
23) The fact that the rules about mask wearing vary from place to place proves that there is no `science’ behind the advice to wear masks. So, for example, why should the coronavirus spread from person to person in a shop but not in an office?
24) There were no mask requirements in Sweden, and the mortality rate there remained below a bad flu season. The average age of Swedish citizens who died of covid-19 was well over 80 years.
25) A meta-analysis of controlled trials of face masks published in May 2020 by the Centers for Disease Control in the US, concluded that masks `did not support a substantial effect on transmission of laboratory confirmed influenza, either when worn by infected persons or by persons in the general community to reduce their susceptibility’.
26) A meta- analysis published in May 2016 concluded that masks did not have any useful effect but that reuse of contaminated masks did transmit infection.
27) In 2019, a paper involving 2,862 volunteers and published in the Journal of the American Medical Association showed that both surgical masks and N95 respirators `resulted in no significant difference in the incidence of laboratory confirmed influenza’.
28) In 2011, a meta-analysis of 17 separate studies showed that none of the research showed masks to be useful in preventing influenza infection.
29) In 2009, a paper published in the Journal of Occupational Environmental Hygiene concluded that particles passed through masks and that expelled particles were deflected around the edges of masks.
30) Research published in 2005 concluded that there was more transmission of virus laden particles from masked individuals than from unmasked individuals because of `leakage’ jets of air. Backward unfiltered air flow was found to be stronger with mask wearers (suggesting that standing behind someone wearing a mask could be dangerous).
31) A study published in the BMJ in 2015 found that the penetration of cloth masks was almost 97%.
32) N95 masks are made with a 0.3 micron filter. The name comes from the fact that 95% of particles having a diameter of 0.3 microns are filtered by the mask. Unfortunately, coronaviruses are approximately 0.125 microns in diameter.
33) An article entitled `Is a mask necessary in the operating theatre?’, published in the Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons in 1981 found no difference in wound infection rates with or without surgical masks. A paper published in 1991 showed that the use of masks slightly increased the incidence of infection.
34) It was proved in 1920 that cloth masks do not stop flu transmission. It was concluded then that the number of layers of fabric required to prevent pathogen spread would be suffocating. It was also recognised that there was a problem with leakage around the edges of masks.
35) Mask wearers are encouraged to demonise non-mask wearers (even if they are disabled in some way). This is part of the psychological warfare battle being fought.
36) There have been suggestions from various authorities that mask wearing and social distancing will need to be permanent. It has also been suggested that masks should be worn in the home.
37) Masks collect fungi, bacteria and viruses and because of the moist air exhaled they are an excellent breeding ground.
38) `We know that wearing a mask outside health care facilities offer little, if any, protection from infection…In many cases the desire for widespread masking is a reflexive reaction to anxiety over the pandemic.’ – New England Journal of Medicine, 2020
39) Research published in June 2020 suggested that the reduction in blood oxygen and the increase in carbon dioxide, resulting from mask wearing, might cause a strain on the heart and kidneys.
40) Mask wearers are more likely to develop infection than non-mask wearers. This may be due to the fact that masks reduce blood oxygen levels and adversely affect natural immunity. It is likely that anyone who wears a face mask for long periods will have a damaged immune system – and be more susceptible to infection. Studies have shown that hypoxia can inhibit immune cells used to fight viral infections. Wearing a mask may make the wearer more likely to develop an infection – and if an infection develops it is likely to be worse.
41) Masks can cause hypercapnia (increased carbon dioxide). Symptoms of hypercapnia include drowsiness, dizziness and fatigue.
42) A mask worn by a child in school was examined in a laboratory. Tests showed 82 bacterial colonies and 4 mould colonies growing on the mask.
43) In May 2020, Dr Fauci, the American covid-19 expert, concluded that masks are little more than symbolic – virtue signaling.
44) Although they have not been tested extensively, visors are probably just as useless as masks but they may be less dangerous to wearers.
Truths about Masks that Politicians and the BBC Probably Forgot to Mention
1) Face masks have been proven to do harm but not proven to do good. Forcing citizens to wear them is a form of oppression. Support for mask wearing comes from individuals promoting face masks for political rather than health reasons. There is now considerable support for masks to be worn out of doors and even in the home. There is absolutely no scientific reason for this.
2) Over a dozen scientific papers show clearly that masks are ineffective in preventing the movement of infective organisms. They also reduce oxygen levels and expose wearers to increased levels of carbon dioxide.
3) Nine medical authors from Australia and Vietnam studied cloth face masks and concluded that cloth masks should not be recommended for health care workers.
4) Wearing a mask for long periods could cause pulmonary fibrosis. Loose fibres are seen on all types of masks and may be inhaled causing serious lung damage.
5) Researchers in France proved that wearing a surgical mask causes breathlessness.
6) Masks should be changed every couple of hours and old masks should be disposed of safely. If cloth masks are worn, they should be washed at high temperatures twice a day. Disposable masks should be discarded after one use. (Masks thrown down in the street are a serious health hazard.)
7) Evidence proving the danger and ineffectiveness of masks has been banned, blocked or deleted. Discussion and debate about the value of face masks is suppressed.
8) In September 2020, 70 Belgian doctors claimed that mandatory face masks in schools are a major threat to child development.
9) A leading German virologist claims that face masks are a wonderful breeding ground for bacteria and fungi.
10) Dentists in New York have reported that mask wearing causes gum disease and dental cavities. The dentists say that face coverings lead to mouth dryness and an increase in the build-up of bacteria.
11) Exemption certificates/cards can be obtained online for those who are unable to wear a mask.
12) Some face masks may have pores five thousand times larger than virus particles.
13) Masks should never be touched once in place. If a mask is touched it must be replaced immediately.
14) No one should wear a mask while exercising. There have been several reports of masked children dying while exercising. There is evidence showing that mask wearing reduces blood oxygen levels even when the wearer is standing still. Individuals who exercise are likely to sweat. Masks then become damp more quickly and the damp promotes the growth of microorganisms.
15) There is a risk that viruses may accumulate in the fabric of a mask – thereby increasing the amount of the virus being inhaled.
16) Putting a mask on a baby or unconscious patient is dangerous. The mask may result in the wearer choking on vomit.
17) Some of the carbon dioxide exhaled with each breath is trapped behind the mask.
18) One study of health workers wearing masks showed that a third developed headaches requiring painkillers. Another study showed that 81% developed headaches – and their work was affected.
19) A mask can reduce blood oxygenation by up to 20% – leading to a possible loss of consciousness. At least one road crash has been blamed on a driver wearing a mask. Police reported that the driver of a single car crash in New Jersey is believed to have passed out behind the wheel after wearing a mask for too long.
20) Over a dozen studies failed to show that wearing a mask provides protection against infection.
21) Masks are being used as a conditioning tool to make us more compliant.
22) A study of 53 surgeons showed that there were statistically significant falls in blood oxygen levels after masks had been worn for a few hours. It is important to remember that surgeons who wear masks (and not all do) work while standing, rather than walking, and they work in a controlled, air conditioned environment. They do not touch their masks and they change them regularly.
23) The fact that the rules about mask wearing vary from place to place proves that there is no `science’ behind the advice to wear masks. So, for example, why should the coronavirus spread from person to person in a shop but not in an office?
24) There were no mask requirements in Sweden, and the mortality rate there remained below a bad flu season. The average age of Swedish citizens who died of covid-19 was well over 80 years.
25) A meta-analysis of controlled trials of face masks published in May 2020 by the Centers for Disease Control in the US, concluded that masks `did not support a substantial effect on transmission of laboratory confirmed influenza, either when worn by infected persons or by persons in the general community to reduce their susceptibility’.
26) A meta- analysis published in May 2016 concluded that masks did not have any useful effect but that reuse of contaminated masks did transmit infection.
27) In 2019, a paper involving 2,862 volunteers and published in the Journal of the American Medical Association showed that both surgical masks and N95 respirators `resulted in no significant difference in the incidence of laboratory confirmed influenza’.
28) In 2011, a meta-analysis of 17 separate studies showed that none of the research showed masks to be useful in preventing influenza infection.
29) In 2009, a paper published in the Journal of Occupational Environmental Hygiene concluded that particles passed through masks and that expelled particles were deflected around the edges of masks.
30) Research published in 2005 concluded that there was more transmission of virus laden particles from masked individuals than from unmasked individuals because of `leakage’ jets of air. Backward unfiltered air flow was found to be stronger with mask wearers (suggesting that standing behind someone wearing a mask could be dangerous).
31) A study published in the BMJ in 2015 found that the penetration of cloth masks was almost 97%.
32) N95 masks are made with a 0.3 micron filter. The name comes from the fact that 95% of particles having a diameter of 0.3 microns are filtered by the mask. Unfortunately, coronaviruses are approximately 0.125 microns in diameter.
33) An article entitled `Is a mask necessary in the operating theatre?’, published in the Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons in 1981 found no difference in wound infection rates with or without surgical masks. A paper published in 1991 showed that the use of masks slightly increased the incidence of infection.
34) It was proved in 1920 that cloth masks do not stop flu transmission. It was concluded then that the number of layers of fabric required to prevent pathogen spread would be suffocating. It was also recognised that there was a problem with leakage around the edges of masks.
35) Mask wearers are encouraged to demonise non-mask wearers (even if they are disabled in some way). This is part of the psychological warfare battle being fought.
36) There have been suggestions from various authorities that mask wearing and social distancing will need to be permanent. It has also been suggested that masks should be worn in the home.
37) Masks collect fungi, bacteria and viruses and because of the moist air exhaled they are an excellent breeding ground.
38) `We know that wearing a mask outside health care facilities offer little, if any, protection from infection…In many cases the desire for widespread masking is a reflexive reaction to anxiety over the pandemic.’ – New England Journal of Medicine, 2020
39) Research published in June 2020 suggested that the reduction in blood oxygen and the increase in carbon dioxide, resulting from mask wearing, might cause a strain on the heart and kidneys.
40) Mask wearers are more likely to develop infection than non-mask wearers. This may be due to the fact that masks reduce blood oxygen levels and adversely affect natural immunity. It is likely that anyone who wears a face mask for long periods will have a damaged immune system – and be more susceptible to infection. Studies have shown that hypoxia can inhibit immune cells used to fight viral infections. Wearing a mask may make the wearer more likely to develop an infection – and if an infection develops it is likely to be worse.
41) Masks can cause hypercapnia (increased carbon dioxide). Symptoms of hypercapnia include drowsiness, dizziness and fatigue.
42) A mask worn by a child in school was examined in a laboratory. Tests showed 82 bacterial colonies and 4 mould colonies growing on the mask.
43) In May 2020, Dr Fauci, the American covid-19 expert, concluded that masks are little more than symbolic – virtue signaling.
44) Although they have not been tested extensively, visors are probably just as useless as masks but they may be less dangerous to wearers.
 If you would like something to show store managers, feel free to order one of these mask exemption cards, while supporting a freedom-loving, family-owned business at the same time!
If you would like something to show store managers, feel free to order one of these mask exemption cards, while supporting a freedom-loving, family-owned business at the same time!  1. Surgeons have been using surgical masks since their introduction in 1897. It has for some years been customary for surgeons and nurses to wear surgical masks in the operating theatre and to change masks part of the way through any procedure lasting more than a few hours. The dangers associated with mask wearing were assessed by five doctors and published in the journal Neurocirugia in 2008.
Although it is customary for operating theatres to be fitted with air conditioning systems, the writers of the article, entitled, Preliminary Report on Surgical Mask induced Deoxygenation During Major Surgery, pointed out that it is known that heat and moisture are trapped beneath surgical masks and concluded that ‘it seems reasonable that some of the exhaled carbon dioxide may also be trapped beneath them, inducing a decrease in blood oxygenation’.
A total of 53 surgeons, of both sexes, all employed at university hospitals and aged between 24 and 54 years of age were tested. All were non-smokers and none had any chronic lung disease. The test involved pulse oximetry before and after the course of an operation. The study showed that the longer a mask was worn the greater the fall in blood oxygen levels. This may lead to the individual passing out and it may also affect natural immunity – thereby increasing the risk of infection. The masks used were disposable, sterile, one-way surgical paper masks. To eliminate the effect of dehydration over a several hour surgical operation, the surgeons were allowed after every hour to drink water through a straw.
The authors of the paper concluded that, ‘When the values for oxygen saturation of haemoglobin were compared, there were statistically significant differences only between preoperational and post operational values. As the duration of the operation increases, oxygen saturation of haemoglobin decreases significantly.’
1. Surgeons have been using surgical masks since their introduction in 1897. It has for some years been customary for surgeons and nurses to wear surgical masks in the operating theatre and to change masks part of the way through any procedure lasting more than a few hours. The dangers associated with mask wearing were assessed by five doctors and published in the journal Neurocirugia in 2008.
Although it is customary for operating theatres to be fitted with air conditioning systems, the writers of the article, entitled, Preliminary Report on Surgical Mask induced Deoxygenation During Major Surgery, pointed out that it is known that heat and moisture are trapped beneath surgical masks and concluded that ‘it seems reasonable that some of the exhaled carbon dioxide may also be trapped beneath them, inducing a decrease in blood oxygenation’.
A total of 53 surgeons, of both sexes, all employed at university hospitals and aged between 24 and 54 years of age were tested. All were non-smokers and none had any chronic lung disease. The test involved pulse oximetry before and after the course of an operation. The study showed that the longer a mask was worn the greater the fall in blood oxygen levels. This may lead to the individual passing out and it may also affect natural immunity – thereby increasing the risk of infection. The masks used were disposable, sterile, one-way surgical paper masks. To eliminate the effect of dehydration over a several hour surgical operation, the surgeons were allowed after every hour to drink water through a straw.
The authors of the paper concluded that, ‘When the values for oxygen saturation of haemoglobin were compared, there were statistically significant differences only between preoperational and post operational values. As the duration of the operation increases, oxygen saturation of haemoglobin decreases significantly.’
 2. This quote is taken from New England Journal of Medicine: ‘We know that wearing a mask outside health care facilities offers little, if any, protection from infection. Public health authorities define a significant exposure to covid-19 as face to face contact within six feet with a patient with symptomatic covid-19 that is sustained for at least a few minutes (and some say more than 10 minutes or even 20 minutes). The chance of catching covid-19 from a passing interaction in a public space is therefore minimal. In many cases the desire for widespread masking is a reflexive reaction to anxiety over the pandemic.’ The reference is: M.Klompas, C.Morris et al ‘Universal Masking in hospitals in the covid-19 era’ – New
England Journal of Medicine 2020
2. This quote is taken from New England Journal of Medicine: ‘We know that wearing a mask outside health care facilities offers little, if any, protection from infection. Public health authorities define a significant exposure to covid-19 as face to face contact within six feet with a patient with symptomatic covid-19 that is sustained for at least a few minutes (and some say more than 10 minutes or even 20 minutes). The chance of catching covid-19 from a passing interaction in a public space is therefore minimal. In many cases the desire for widespread masking is a reflexive reaction to anxiety over the pandemic.’ The reference is: M.Klompas, C.Morris et al ‘Universal Masking in hospitals in the covid-19 era’ – New
England Journal of Medicine 2020
 3. It is possible that wearing a mask for hours at a time could cause pulmonary fibrosis. In August 1988, the proceedings of the VIIth International Pneumoconioses Conference included details of three cases of pulmonary fibrosis, thought to be due to exposure to synthetic textile fibres. The first was a woman of 52 who had a dry cough with increasing difficulty in breathing. Changes were visible on an X-ray. The woman had been working in a textile shop for 15 years where her job was measuring and cutting cloth – mainly synthetic materials. The second patient was a woman of 66 who also had difficulty in breathing. The lungs of this patient also showed X-ray changes. She was also involved in cutting and measuring synthetic fabrics. A third woman, aged 47, had bilateral pulmonary fibrosis. Studies have shown that loose fibres are seen on all types of masks and may be inhaled causing serious lung damage.
4.People who cough and sneeze into their mask increase the risk of a build-up of fungi and bacteria – which can lead to dangerous chest infections.
5. In 2015, the British Medical Journal published a paper entitled, A Cluster Randomized Trial of Cloth Masks Compared with Medical Masks in Healthcare Workers. The paper was written by nine authors from the University of New South Wales, the University of Sydney, the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology in Vietnam and the Beijing Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in China. The aim of the study was to compare the efficacy of cloth masks to medical masks in hospital health care workers. The study, which was extensive, concluded that the results caution against the use of cloth masks.
3. It is possible that wearing a mask for hours at a time could cause pulmonary fibrosis. In August 1988, the proceedings of the VIIth International Pneumoconioses Conference included details of three cases of pulmonary fibrosis, thought to be due to exposure to synthetic textile fibres. The first was a woman of 52 who had a dry cough with increasing difficulty in breathing. Changes were visible on an X-ray. The woman had been working in a textile shop for 15 years where her job was measuring and cutting cloth – mainly synthetic materials. The second patient was a woman of 66 who also had difficulty in breathing. The lungs of this patient also showed X-ray changes. She was also involved in cutting and measuring synthetic fabrics. A third woman, aged 47, had bilateral pulmonary fibrosis. Studies have shown that loose fibres are seen on all types of masks and may be inhaled causing serious lung damage.
4.People who cough and sneeze into their mask increase the risk of a build-up of fungi and bacteria – which can lead to dangerous chest infections.
5. In 2015, the British Medical Journal published a paper entitled, A Cluster Randomized Trial of Cloth Masks Compared with Medical Masks in Healthcare Workers. The paper was written by nine authors from the University of New South Wales, the University of Sydney, the National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology in Vietnam and the Beijing Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in China. The aim of the study was to compare the efficacy of cloth masks to medical masks in hospital health care workers. The study, which was extensive, concluded that the results caution against the use of cloth masks.
 ‘This is an important finding to inform occupational health and safety,’ concluded the authors. ‘Moisture retention, reuse of cloth masks and poor filtration may result in increased risk of infection.’ And the authors added: ‘…as a precautionary measure, cloth masks should not be recommended for health care workers, particularly in high risk situations, and guidelines need to be updated’.
For the remaining 95 facts, click here!
Source: Dr. Vernon Coleman
‘This is an important finding to inform occupational health and safety,’ concluded the authors. ‘Moisture retention, reuse of cloth masks and poor filtration may result in increased risk of infection.’ And the authors added: ‘…as a precautionary measure, cloth masks should not be recommended for health care workers, particularly in high risk situations, and guidelines need to be updated’.
For the remaining 95 facts, click here!
Source: Dr. Vernon Coleman 
Please read the fine print of this vax and decide for yourself:
https://www.fda.gov/media/144245/download? fbclid=IwAR1CaTeZDaeXTwZzcJfncaMviDxZ3LAx40thbLQjEWEOILSFFbm80Q6o3Yk 
Dr. Roger Hodkinson, Chairman of the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons committee in Ottawa, CEO of a large private medical laboratory in Edmonton, Alberta and Chairman of a Medical Biotechnology company SELLING THE COVID-19 TEST:
"There is utterly unfounded public hysteria driven by the media and politicians. This is the biggest hoax ever perpetrated on an unsuspected public. There is absolutely nothing that can be done to contain this virus. This is nothing more than a bad flu season. It's politics playing medicine and that's a very dangerous game. There is no action needed...Masks are utterly useless. There is no evidence whatsoever they are even effective. It is utterly ridiculous seeing these unfortunate, uneducated people walking around like lemmings obeying without any evidence. Social distancing is also useless... The risk of death under 65 is 1 in 300,000...response is utterly ridiculous."
 So, we shut the world down... for what?? I’m jumping all over the place in this post, so bear with me.
"Since no quantified virus isolates of the 'virus' are currently available, assays designed for detection of the 'virus' were tested with characterized stocks of in vitro transcribed full length RNA (N gene; GenBank accession: MN908947.2) of known titer (RNA copies/µL) spiked into a diluent consisting of a suspension of human A549 cells and viral transport medium (VTM) to mimic clinical specimen."
Aka, the test is looking for RNA, which is presumed to come from the virus that hasn't been proven to exist. Yes, people are getting sick, but from what... if this particular virus hasn't been isolated? The CDC says it isn't available. Source: https://www.fda.gov/media/134922/download (page 39)
Think they wouldn't trick us with a virus? Have you researched the Bird Flu in relation to Agent Orange? Try finding Dr. Sherri Tenpenny’s book Fowl for more info. So many questions. I digress. I do that a lot. So how are we hearing about so. many. cases?
A positive test result does NOT equal a case. A positive test simply means, at some point, there was a viral infection, but it’s more than likely been removed... due to our beautiful, God-given immune systems. In fact, it’s safe to say that the the inventor of the PCR test, Dr. Kary Mullis, a Nobel peace prize winner, would be outspoken against people like Dr. Fauci, if he were still alive today. We know that he was a thorn in the side of the establishment during the HIV/AIDS debate.
So, we shut the world down... for what?? I’m jumping all over the place in this post, so bear with me.
"Since no quantified virus isolates of the 'virus' are currently available, assays designed for detection of the 'virus' were tested with characterized stocks of in vitro transcribed full length RNA (N gene; GenBank accession: MN908947.2) of known titer (RNA copies/µL) spiked into a diluent consisting of a suspension of human A549 cells and viral transport medium (VTM) to mimic clinical specimen."
Aka, the test is looking for RNA, which is presumed to come from the virus that hasn't been proven to exist. Yes, people are getting sick, but from what... if this particular virus hasn't been isolated? The CDC says it isn't available. Source: https://www.fda.gov/media/134922/download (page 39)
Think they wouldn't trick us with a virus? Have you researched the Bird Flu in relation to Agent Orange? Try finding Dr. Sherri Tenpenny’s book Fowl for more info. So many questions. I digress. I do that a lot. So how are we hearing about so. many. cases?
A positive test result does NOT equal a case. A positive test simply means, at some point, there was a viral infection, but it’s more than likely been removed... due to our beautiful, God-given immune systems. In fact, it’s safe to say that the the inventor of the PCR test, Dr. Kary Mullis, a Nobel peace prize winner, would be outspoken against people like Dr. Fauci, if he were still alive today. We know that he was a thorn in the side of the establishment during the HIV/AIDS debate.
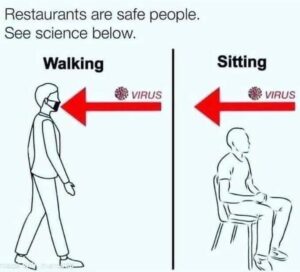 If suffering from emphysema, bronchiectasis, or low O2 saturation, you won't do well - and if allergic to the chemicals (Teflon much?) in the mask, you'll find it especially difficult.
If suffering from emphysema, bronchiectasis, or low O2 saturation, you won't do well - and if allergic to the chemicals (Teflon much?) in the mask, you'll find it especially difficult.
 And then there’s this from the WHO: no lockdowns. I just can’t keep up with their “agenda science." What's up their sleeve? https://t.co/gv93wd5gc5
So, how does a virus work, you ask? https://www.thebernician.net/
And then there’s this from the WHO: no lockdowns. I just can’t keep up with their “agenda science." What's up their sleeve? https://t.co/gv93wd5gc5
So, how does a virus work, you ask? https://www.thebernician.net/
I research bioweapons... and masks. In my professional career, I've never heard anybody actually believe that any kind of mask, short of an actual level 4 containment suit, made a difference to small particle viruses. In fact, the CDC itself just published an article in May exactly saying that... You cannot contain influenza with these masks, and that's even larger than this virus. I've reviewed all the science... My conclusion, redoing my investigation this time, is that people that are now purporting to scientifically prove masks work are either being paid or being played. This just doesn't work this way. And... the outcome of this is not going to be good. -Dr. Lee Merritt, M.DFull video:
 I asked if you noticed a change in people regarding masks. And after reading responses (sorry I couldn’t fit them all), I think it’s safe to say that these 𝙇𝙤𝙫𝙚-𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧-𝙣𝙚𝙞𝙜𝙝𝙗𝙤𝙧 -𝙅𝙪𝙨𝙩-𝙬𝙚𝙖𝙧-𝙩𝙝𝙚-&$@!-𝙢𝙖𝙨𝙠-𝙏𝙝𝙚𝙮-𝙬𝙤𝙣’𝙩-𝙝𝙪𝙧𝙩-𝙮𝙤𝙪 face coverings are bringing out the worst in people. Seems Cathy O’Brien, survivor of MK Ultra mind control and author of TRANCE Formation of America, had it right.
I asked if you noticed a change in people regarding masks. And after reading responses (sorry I couldn’t fit them all), I think it’s safe to say that these 𝙇𝙤𝙫𝙚-𝙮𝙤𝙪𝙧-𝙣𝙚𝙞𝙜𝙝𝙗𝙤𝙧 -𝙅𝙪𝙨𝙩-𝙬𝙚𝙖𝙧-𝙩𝙝𝙚-&$@!-𝙢𝙖𝙨𝙠-𝙏𝙝𝙚𝙮-𝙬𝙤𝙣’𝙩-𝙝𝙪𝙧𝙩-𝙮𝙤𝙪 face coverings are bringing out the worst in people. Seems Cathy O’Brien, survivor of MK Ultra mind control and author of TRANCE Formation of America, had it right.
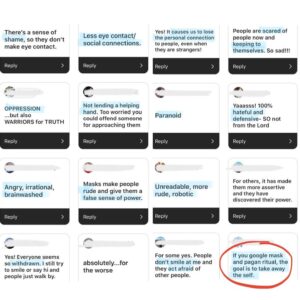 "𝐌𝐚𝐬𝐤𝐬 𝐝𝐞𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐨𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐢𝐳𝐞 𝚠𝚑𝚒𝚕𝚎 𝚖𝚊𝚔𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚊 𝚙𝚎𝚛𝚜𝚘𝚗 𝚏𝚎𝚎𝚕 𝚊𝚜 𝚝𝚑𝚘𝚞𝚐𝚑 𝚝𝚑𝚎𝚢 𝚑𝚊𝚟𝚎 𝚗𝚘 𝚟𝚘𝚒𝚌𝚎. 𝙸𝚝 𝚒𝚜 𝚊 𝚋𝚊𝚛𝚛𝚒𝚎𝚛 𝚝𝚘 𝚘𝚝𝚑𝚎𝚛𝚜... 𝙼𝚊𝚜𝚔𝚜 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚖𝚒𝚗𝚍 𝚏𝚛𝚘𝚖 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚘𝚞𝚝𝚜𝚒𝚍𝚎 𝚒𝚗, 𝚕𝚒𝚔𝚎 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚛𝚎𝚍𝚎𝚏𝚒𝚗𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚘𝚏 𝚠𝚘𝚛𝚍𝚜 𝚒𝚜 𝚍𝚘𝚒𝚗𝚐. 𝙱𝚢 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕𝚕𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚠𝚑𝚊𝚝 𝚠𝚎 𝚌𝚊𝚗 𝚊𝚗𝚍 𝚌𝚊𝚗𝚗𝚘𝚝 𝚜𝚊𝚢 𝚏𝚘𝚛 𝚏𝚎𝚊𝚛 𝚘𝚏 𝚋𝚎𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚕𝚊𝚋𝚎𝚕𝚎𝚍 𝚛𝚊𝚌𝚒𝚜𝚝 𝚘𝚛 𝚋𝚎𝚊𝚝𝚎𝚗, 𝚏𝚘𝚛 𝚎𝚡𝚊𝚖𝚙𝚕𝚎, 𝐢𝐭 𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐥𝐲 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐥𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐮𝐠𝐡𝐭 𝐭𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐝𝐫𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐥𝐲 𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬 (𝚘𝚛 𝚕𝚊𝚌𝚔 𝚝𝚑𝚎𝚛𝚎𝚘𝚏). 𝙻𝚒𝚔𝚎𝚠𝚒𝚜𝚎, 𝚊 𝚖𝚊𝚜𝚔 𝚖𝚞𝚏𝚏𝚕𝚎𝚜 𝚘𝚞𝚛 𝚜𝚙𝚎𝚎𝚌𝚑 𝚜𝚘 𝚝𝚑𝚊𝚝 𝚠𝚎 𝚊𝚛𝚎 𝚗𝚘𝚝 𝚑𝚎𝚊𝚛𝚍, 𝚠𝚑𝚒𝚌𝚑 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕𝚜 𝚟𝚘𝚒𝚌𝚎…𝚠𝚘𝚛𝚍𝚜…𝚖𝚒𝚗𝚍. 𝚃𝚑𝚒𝚜 𝚒𝚜 𝙼𝚒𝚗𝚍 𝙲𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕... 𝙋𝙚𝙤𝙥𝙡𝙚 𝙝𝙖𝙫𝙚 𝙨𝙩𝙤𝙥𝙥𝙚𝙙 𝙩𝙖𝙡𝙠𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙬𝙞𝙩𝙝 𝙚𝙖𝙘𝙝 𝙤𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙧 𝚠𝚑𝚒𝚕𝚎 𝚖𝚎𝚍𝚒𝚊 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕𝚜 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚗𝚊𝚛𝚛𝚊𝚝𝚒𝚟𝚎."
"𝐌𝐚𝐬𝐤𝐬 𝐝𝐞𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐨𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐢𝐳𝐞 𝚠𝚑𝚒𝚕𝚎 𝚖𝚊𝚔𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚊 𝚙𝚎𝚛𝚜𝚘𝚗 𝚏𝚎𝚎𝚕 𝚊𝚜 𝚝𝚑𝚘𝚞𝚐𝚑 𝚝𝚑𝚎𝚢 𝚑𝚊𝚟𝚎 𝚗𝚘 𝚟𝚘𝚒𝚌𝚎. 𝙸𝚝 𝚒𝚜 𝚊 𝚋𝚊𝚛𝚛𝚒𝚎𝚛 𝚝𝚘 𝚘𝚝𝚑𝚎𝚛𝚜... 𝙼𝚊𝚜𝚔𝚜 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚖𝚒𝚗𝚍 𝚏𝚛𝚘𝚖 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚘𝚞𝚝𝚜𝚒𝚍𝚎 𝚒𝚗, 𝚕𝚒𝚔𝚎 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚛𝚎𝚍𝚎𝚏𝚒𝚗𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚘𝚏 𝚠𝚘𝚛𝚍𝚜 𝚒𝚜 𝚍𝚘𝚒𝚗𝚐. 𝙱𝚢 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕𝚕𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚠𝚑𝚊𝚝 𝚠𝚎 𝚌𝚊𝚗 𝚊𝚗𝚍 𝚌𝚊𝚗𝚗𝚘𝚝 𝚜𝚊𝚢 𝚏𝚘𝚛 𝚏𝚎𝚊𝚛 𝚘𝚏 𝚋𝚎𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝚕𝚊𝚋𝚎𝚕𝚎𝚍 𝚛𝚊𝚌𝚒𝚜𝚝 𝚘𝚛 𝚋𝚎𝚊𝚝𝚎𝚗, 𝚏𝚘𝚛 𝚎𝚡𝚊𝚖𝚙𝚕𝚎, 𝐢𝐭 𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐥𝐲 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐥𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐮𝐠𝐡𝐭 𝐭𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐝𝐫𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐰𝐨𝐫𝐝𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐢𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐥𝐲 𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐬 (𝚘𝚛 𝚕𝚊𝚌𝚔 𝚝𝚑𝚎𝚛𝚎𝚘𝚏). 𝙻𝚒𝚔𝚎𝚠𝚒𝚜𝚎, 𝚊 𝚖𝚊𝚜𝚔 𝚖𝚞𝚏𝚏𝚕𝚎𝚜 𝚘𝚞𝚛 𝚜𝚙𝚎𝚎𝚌𝚑 𝚜𝚘 𝚝𝚑𝚊𝚝 𝚠𝚎 𝚊𝚛𝚎 𝚗𝚘𝚝 𝚑𝚎𝚊𝚛𝚍, 𝚠𝚑𝚒𝚌𝚑 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕𝚜 𝚟𝚘𝚒𝚌𝚎…𝚠𝚘𝚛𝚍𝚜…𝚖𝚒𝚗𝚍. 𝚃𝚑𝚒𝚜 𝚒𝚜 𝙼𝚒𝚗𝚍 𝙲𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕... 𝙋𝙚𝙤𝙥𝙡𝙚 𝙝𝙖𝙫𝙚 𝙨𝙩𝙤𝙥𝙥𝙚𝙙 𝙩𝙖𝙡𝙠𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙬𝙞𝙩𝙝 𝙚𝙖𝙘𝙝 𝙤𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙧 𝚠𝚑𝚒𝚕𝚎 𝚖𝚎𝚍𝚒𝚊 𝚌𝚘𝚗𝚝𝚛𝚘𝚕𝚜 𝚝𝚑𝚎 𝚗𝚊𝚛𝚛𝚊𝚝𝚒𝚟𝚎."
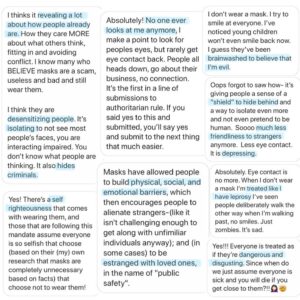 He who controls the minds of the masses, wins (Operation Mockingbird). Remember, God has given His children the spirit of power, love, and a sound mind. Fear is a spirit. And it is not from God.
He who controls the minds of the masses, wins (Operation Mockingbird). Remember, God has given His children the spirit of power, love, and a sound mind. Fear is a spirit. And it is not from God.
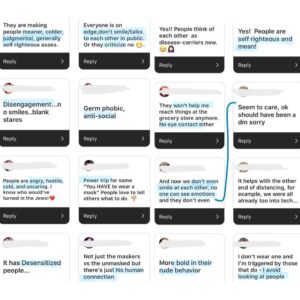
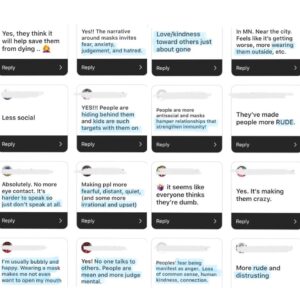
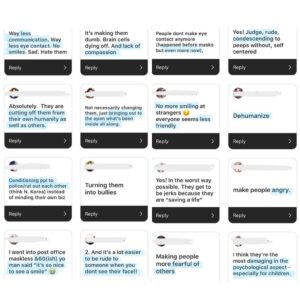
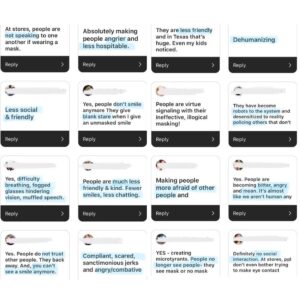 Some have said that Christ followers need to suck it up because it’s the simple act of not wearing a mask that is unkind. However, your messages tell a different story. It seems the majority of hateful words are being hurled by those who’ve been convinced that mask wearing saves lives. The science simply doesn’t support that perspective, but we’ve covered that to exhaustion.
“Love is kind. If it’s not, it’s something else.” - Bob Goff
Some have said that Christ followers need to suck it up because it’s the simple act of not wearing a mask that is unkind. However, your messages tell a different story. It seems the majority of hateful words are being hurled by those who’ve been convinced that mask wearing saves lives. The science simply doesn’t support that perspective, but we’ve covered that to exhaustion.
“Love is kind. If it’s not, it’s something else.” - Bob Goff
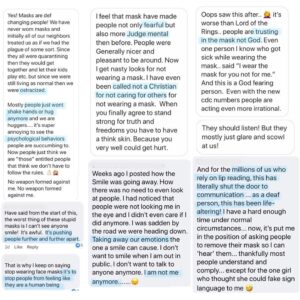
 Aware of a bigger agenda, 𝐚𝐭 𝐰𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐩𝐨𝐢𝐧𝐭 𝐝𝐨𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐛𝐞𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐞 𝐮𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐨 𝐠𝐨 𝐚𝐥𝐨𝐧𝐠 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐢𝐞𝐬? SO many lies. The tactic for confusion is to throw us into chaos so that we beg for order (aka, more gov’t control). Anything to go back to “normal”. As Cathy says, “knowledge is our first line of defense against mind control.” It’s time for the great unmasking... And a return to kindness, chivalry, and compassion towards others.
Aware of a bigger agenda, 𝐚𝐭 𝐰𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐩𝐨𝐢𝐧𝐭 𝐝𝐨𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐭 𝐛𝐞𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐞 𝐮𝐧𝐥𝐨𝐯𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐨 𝐠𝐨 𝐚𝐥𝐨𝐧𝐠 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐢𝐞𝐬? SO many lies. The tactic for confusion is to throw us into chaos so that we beg for order (aka, more gov’t control). Anything to go back to “normal”. As Cathy says, “knowledge is our first line of defense against mind control.” It’s time for the great unmasking... And a return to kindness, chivalry, and compassion towards others.
 I’m praying for:
Eyes to see
Ears to hear
Humble hearts
Kindness restored
Hope renewed
Christ revealed
Souls saved
Amen!
woketxmama
⠀⠀⠀ ⠀
Source: @realcathyobrien
https://trance-formation.com/the-great-unmasking/
I’m praying for:
Eyes to see
Ears to hear
Humble hearts
Kindness restored
Hope renewed
Christ revealed
Souls saved
Amen!
woketxmama
⠀⠀⠀ ⠀
Source: @realcathyobrien
https://trance-formation.com/the-great-unmasking/