Cloth masks:
26 — S Rengasamy, B Eimer, et al. Simple respiratory protection – evaluation of the filtration performance of cloth masks and common fabric materials against 20-1000 nm size particles. Ann Occup Hyg. 2010 Oct; 54(7): 789-798.
https://academic.oup.com/annweh/article/54/7/789/202744
Original article – cloth masks were found to have low efficiency for blocking particles of 0.3 microns and smaller. Aerosol penetration through the various cloth masks examined in the is study were between 74 and 90%. Likewise, the filtration efficiency of fabric materials was 3% to 33%.
27 — C MacIntyre, H Seale, et al. A cluster randomized trial of cloth masks compared with medical masks in healthcare workers. BMJ Open. 2015; 5(4)
https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/5/4/e006577.long
Randomised controlled trial – healthcare workers wearing cloth masks were found to have 13 times the risk of influenza-like illness than those wearing medical masks.
28 — W Kellogg. An experimental study of the efficacy of gauze face masks. Am J Pub Health. 1920. 34-42.
https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/pdf/10.2105/AJPH.10.1.34
Original article – 1920 – analysis of cloth mask use during the 1918 pandemic examines the failure of masks to impede or stop flu transmission at that time. Concluded that the number of layers of fabric required to prevent pathogen penetration would have required a suffocating number of layers, and could not be used for that reason, as well as the problem of leakage vents around the edges of cloth masks.
29 — Lindsley WG, Blachere FM, Beezhold DH, et al. A comparison of performance metrics for cloth face masks as source control devices for simulated cough and exhalation aerosols. Preprint. medRxiv. 2021;2021.02.16.21251850. Published 2021 Feb 19. doi:10.1101/2021.02.16.21251850
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7899465/
Masks against Covid-19:
29 — M Klompas, C Morris, et al. Universal masking in hospitals in the Covid-19 era. N Eng J Med. 2020; 382 e63.
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMp2006372
Editorial New England Journal of Medicine – “we know that wearing a mask outside health care facilities offers little, if any, protection from infection. Public health authorities define a significant exposure to Covid-19 as face-to-face contact within 6 feet with a patient with symptomatic Covid-19 that is sustained for at least a few minutes (and some say more than 10 minutes or even 20 minutes). The chance of catching Covid-19 from a passing interaction in a public space therefore is minimal. In many cases, the desire for widespread masking is a reflexive reaction to anxiety over the pandemic.”
SAFETY OF MASKS
During walking or other exercise
30 — E Person, C Lemercier et al. Effect of a surgical mask on six minute walking distance. Rev Mal Respir. 2018 Mar; 35(3):264-268.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29395560/
Randomised controlled trial – surgical mask wearers had significantly increased dyspnea after a 6 minute walk than non-mask wearers.
31 — B Chandrasekaran, S Fernandes. Exercise with facemask; are we handling a devil’s sword – a physiological hypothesis. Med Hypothese. 2020 Jun 22. 144:110002.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32590322/
Physiological Hypothesis – concern about possible burden of facemasks during physical activity on pulmonary, circulatory and immune systems, due to oxygen reduction and air trapping reducing substantial carbon dioxide exchange. As a result of hypercapnia, there may be a cardiac overload, renal overload and a shift to metabolic acidosis.
Risks of N95 respirators:
32 — P Shuang Ye Tong, A Sugam Kale, et al. Respiratory consequences of N95-type mask usage in pregnant healthcare workers – A controlled clinical study. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2015 Nov 16; 4:48.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26579222/
Controlled clinical trial – Pregnant healthcare workers were found to have a loss in volume of oxygen consumption by 13.8% compared to controls when wearing N95 respirators. 17.7% less carbon dioxide was inhaled.
33 — T Kao, K Huang, et al. The physiological impact of wearing an N95 mask during hemodialysis as a precaution against SARS in patients with end-stage renal disease. J Formos Med Assoc. 2004 Aug; 103(8):624-628.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15340662/
Original article – patients with end stage renal disease were studied during use of N95 respirators. Their partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) decreased significantly compared to controls and increased respiratory adverse effects. 19% of the patients developed various degrees of hypoxemia while wearing the masks.
34 — F Blachere, W Lindsley et al. Assessment of influenza virus exposure and recovery from contaminated surgical masks and N95 respirators. J Viro Methods. 2018 Oct; 260:98-106.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30029810/
Original article – healthcare workers’ N95 respirators were measured by personal bioaerosol samplers to harbor influenza virus.
35 — A Rule, O Apau, et al. Healthcare personnel exposure in an emergency department during influenza season. PLoS One. 2018 Aug 31; 13(8): e0203223.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30169507/
Original article – 25% of healthcare workers’ facepiece respirators were found to contain influenza in an emergency department during the 2015 flu season.
Risk of surgical masks:
36 — F Blachere, W Lindsley et al. Assessment of influenza virus exposure and recovery from contaminated surgical masks and N95 respirators. J Viro Methods. 2018 Oct; 260:98-106.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30029810/
Original article – healthcare workers’ surgical masks were measured by personal bioaerosol samplers to harbour for influenza virus.
37 — A Chughtai, S Stelzer-Braid, et al. Contamination by respiratory viruses on our surface of medical masks used by hospital healthcare workers. BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jun 3; 19(1): 491.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31159777/
Original clinical study – various respiratory pathogens were found on the outer surface of used medical masks, which could result in self-contamination. The risk was found to be higher with the longer duration of mask use.
38 — L Zhiqing, C Yongyun, et al. J Orthop Translat. 2018 Jun 27; 14:57-62.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30035033/
Original article – surgical masks were found to be a repository of bacterial contamination. The source of the bacterial was determined to be the body surface of the surgeons, rather than the operating room environment. Given that surgeons are gowned from head to food for surgery, this finding should be especially concerning for the general public who wear masks. Without the protective outfits of surgeons, the general public have even more exposed body surface to serve as a source for bacteria to collect on their masks.
Risks of cloth masks:
39 — C MacIntyre, H Seale, et al. A cluster randomized trial of cloth masks compared with medical masks in healthcare workers. BMJ Open. 2015; 5(4)
https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/5/4/e006577
Randomized controlled trial – healthcare workers wearing cloth masks had significantly higher rates of influenza-like illness after four weeks of continuous on-the-job use, when compared to controls (medical masks)
40 — A Beder, U Buyukkocak, et al. Preliminary report on surgical mask induced deoxygenation during major surgery. Neurocirugia. 2008; 19: 121-126.
http://scielo.isciii.es/pdf/neuro/v19n2/3.pdf
Longitudinal and observational study – increased rate of infection in mask-wearers may be due to a weakening of immune function during mask use. Surgeons were found to have lower oxygen saturation after surgeries even as short as 30 minutes.
41 — D Lukashev, B Klebanov, et al. Cutting edge: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha and its activation[1]inducible short isoform negatively regulate functions of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2006 Oct 15; 177(8) 4962-4965.
https://www.jimmunol.org/content/177/8/4962
Animal study – low oxygen induces hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1).
42 — A Sant, A McMichael. Revealing the role of CD4+ T-cells in viral immunity. J Exper Med. 2012 Jun 30; 209(8):1391-1395.
https://europepmc.org/article/PMC/3420330
Review – low oxygen and induction of HIF-1 down regulates CD4+ T-cells. CD4+ T-cells are necessary for viral immunity.
Maskne:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ijd.15425
https://www.brighteon.com/34ca1629-556b-4d8b-909e-efa43600e277
A few more studies (some repeats) via Dr. Tenpenny:
https://vaxxter.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/07/Masks-Final.pdf

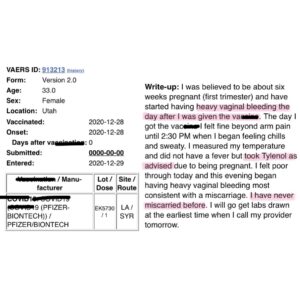
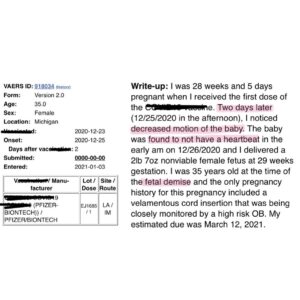




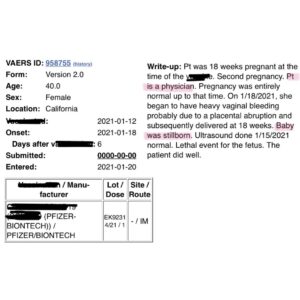
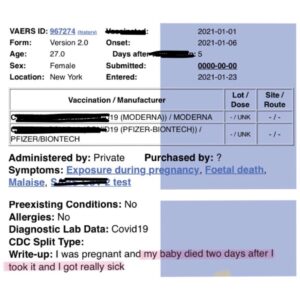
 This… and so many more. Lord, help us.
This… and so many more. Lord, help us.